

Background
Sodium Dodecyl
Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel
Electrophoresis, or SDS-Page, is a scientific technique used to
separate different molecules from one another. Polyacrylamide is a
porous gel matrix that allows molecules to travel through based on size. The
largest molecules separate out near the top of the gel and as the molecules get
smaller they travel further down the gel. Typically, polyacrylamide is the
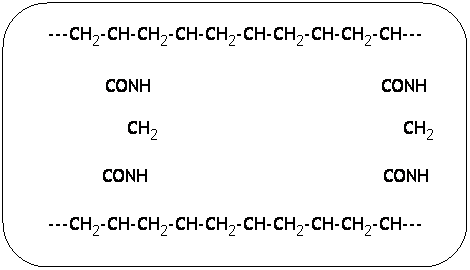
matrix of choice when the goal is to separate most proteins and oligonucleotides. The chemical formula for polyacrylamide gel is shown
below. ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The chains running lengthwise are what determine
the speed at which molecules travel through the gel. Naturally, the more
that are added, the smaller the molecule must be to pass through.
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) is a non-ionic detergent. It's main function to denature the proteins, particularly those in globular or other cumbersome forms, turning them into long polypeptide chains. This puts all of the molecules on an "even playing field," so they are able to separate based on size and not be hindered by shape or conformation.
After they are loaded on the gel and the power source is applied, the desired molecules run through a stacking gel (approximately 2-5% polyacrylamide, pH 6.9) to line up and "prepare" for separation. The molecules then enter a resolving gel (approximately 15% polyacrylamide, pH 8.9). This is where the actual separation occurs.
Following separation, the gel is stained and a photo is taken for analysis.
Sources
SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
(SDS-PAGE)
http://www.mcb.uct.ac.za/sdspage.html
Protocol
1) Obtain sample containing GFP protein
(we used samples from the Hydrophobic Interaction Column and
Size Exclusion Column)
2) Label microcentrifuge tubes
3) 10μL of each sample was placed into the appropriate tube
4) An equal amount (i.e., 10μL) of SDS-loading buffer was added to each tube.
5) Boil the samples for 2 minutes*
6) Add 5μL of loading dye to each sample and centrifuge
7) Quickly plunge the samples into ice for approximately 5-10 seconds.
8) Carefully load samples onto the gel, see example below:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| empty | K1 | Known 1 | Known 2 | Size Ex 3 | Size Ex 2 | HIC | K1 | K2 | empty |
| n/a | 4.5μL | 17μL | 17μL | 17μL | 17μL | 17μL | 4.5μL | 4.5μL | n/a |
8) Cover the gel box and apply the power source
9) Attach a power source to the gel box, set voltage to 120v, and let the gel
run for approximately one hour.
*For preparation of standards, start here. We used KaleidoscopeTM Standards from BIO-RAD, noted here as K1 and K2.